Build Use Case Diagram - Exercise Result
You entered:Course Project Use Case Diagram Solution
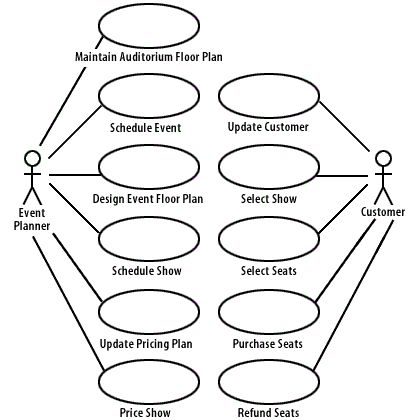
Find the Actors
- Identify the actors by looking for the subjects of the sentences in the problem statement (actor candidates in bold).
Our auditorium is used for different types of events. Some of the events are one-time events, such as basketball games. Other events consist of a number of shows, such as plays or concerts. The event planner can change the floor plan for each event. Some events use the floor for seating (like concerts), and others do not (like basketball games). All the show seating charts for the same event should be based on the same floor plan. The event planner schedules events and shows. Once an event is negotiated, the event planner decides on the floor plan and schedules the individual shows for the event. Once the shows are scheduled, the event planner prices the shows. Pricing is done using a pricing plan. A pricing plan consists of a set of price tiers. Each price tier contains prices for one or more price types: adult, senior, student, and child. The event planner assigns each price tier to a group of seats in a show, one tier per seat. The event planner may also add one or more discounts to the show to try to improve sales. Customers can purchase seats online. Once they provide us with their mailing address, they can look up shows and select the seats they want to reserve. Customers may pay only by credit card payments. If they want refunds, we will credit the card used to purchase the ticket.
- Evaluate what you find and decide whether or not it represents an actor (actors in bold).
Candidate Actor Decision Auditorium Not an actor; an object managed by an event planner Event Not an actor; an object managed by an event planner Show seating chart Not an actor; part of a show Event planner Actor: A person using the other objects found so far, appears many times as an active participant in the problem domain Pricing Not an actor; a noun form of the action “to price” Pricing plan Not an actor; an object managed by an event planner Price tier Not an actor; part of a pricing plan Customer Actor: A person who uses the system for queries and to purchase tickets Credit card Not an actor; an object owned and used by a customer They Customer We The booking system -
Place the actors on the use case diagram (see diagram above).
Find the use cases. - Identify the use cases by looking for actions (verbs) in the problem statement (actions in bold).
Our auditorium is used for different types of events. Some of the events are one-time events, such as basketball games. Other events consist of a number of shows, such as plays or concerts.
The event planner can change the floor plan for each event. Some events use the floor for seating (like concerts), and others do not(like basketball games). All the show seating charts for the same event should be based on the same floor plan.
The event planner schedules events and shows. Once an event is negotiated, the event planner decides on the floor plan and schedules the individual shows for the event. Once the shows are scheduled, the event planner prices the shows.
Pricing is done using a pricing plan. A pricing plan consists of a set of price tiers. Each price tier contains prices for one or more price types: adult, senior, student, and child. The event planner assigns each price tier to a group of seats in a show, one tier per seat. The event planner may also add one or more discounts to the show to try to improve sales.
Customers can purchase seats online. Once they provide us with their mailing address, they can look up shows and select the seats they want to reserve. Customers may pay only by credit card payments. If they want refunds, we will credit the card used to purchase the ticket. - Evaluate the actions to decide whether or not they make good use cases.
Candidate Verb Phrase Evaluation Use Case Auditorium is used for events Identifies the facility in which the events are held Maintain auditorium floor plan Event consists of shows Helps define the composition of an event Schedule show Event planner changes floor plan Modifies the auditorium floor plan for a particular event Design event floor plan Event planner schedules events Schedule event Event planner schedules shows Schedule show Event is negotiated Part of the process to set up an event Schedule event Event planner decides on floor plan Part of the process to set up a show seating chart Design event floor plan Event planner schedules shows Schedule show Pricing plan consists of... Describes the composition of a pricing plan Update pricing plan Price tier contains... Describes the composition of a price tier Update pricing plan Event planner assigns price tier Price show Event planner adds discount Price show Customers purchase seats Purchase seats Customers provide address Update customer Customers look up shows Select show Customers select seats Select seats Customers reserve seats Reserving happens when the customer pays for the seats Purchase seats We accept credit card payments Purchase seats They want refunds Refund seats We credit the credit card The credit is applied during the refund Refund seats - Add the use cases to the use case diagram (see diagram above).