| Lesson 6 | Decision |
| Objective | Describe the decision construct. |
Decision Construct in Procedural Programming
Most programs have statements that are to be executed only under certain conditions. The decision[1] construct (also referred to as the selection construct) allows you to do this. For example, consider the following modified version of the GoForARide program:
In this program the statements:
are executed only when the weather is cold. This is indicated in the pseudocode by indenting these two statements beneath the decision statement:
Put on cycling clothes If the weather is cold Put on a jacket Put on tights Go for a ride Remove cycling clothes Take a shower
In this program the statements:
Put on a jacket Put on tights
are executed only when the weather is cold. This is indicated in the pseudocode by indenting these two statements beneath the decision statement:
If the weather is cold
In the next lesson we will look at the repetition construct.
Here is a flowchart for this program. Note how the decision construct allows us to modify the straight sequential flow of execution of a program.
Here is a flowchart for this program. Note how the decision construct allows us to modify the straight sequential flow of execution of a program.
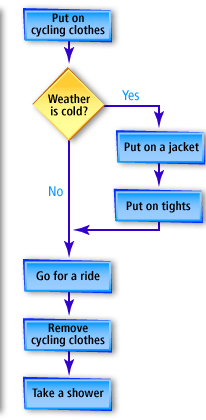
Flowchart Description:
-
Start:
"Put on cycling clothes"
- This is the first action, and it initiates the process.
-
Decision Point:
"Weather is cold?"
- A diamond-shaped decision node checks the weather condition.
-
If "Yes":
- The flow splits rightward and includes two sequential actions:
- "Put on a jacket"
- "Put on tights"
- Then continues to: "Go for a ride"
-
If "No":
- The flow moves directly down to:
- "Go for a ride"
-
Post-ride sequence (for both Yes and No paths):
- "Remove cycling clothes"
- "Take a shower"
Key Observations:
- The flowchart uses a combination of decision nodes and action steps.
- It shows a clear branching logic based on weather conditions.
- Actions converge again after the "Go for a ride" step, making the process unified regardless of temperature after that point.
Here is the equivalent PlantUML code that recreates the cycling flowchart you provided:
🛠 To render this:
@startuml start :Put on cycling clothes; if (Weather is cold?) then (Yes) :Put on a jacket; :Put on tights; endif :Go for a ride; :Remove cycling clothes; :Take a shower; stop @enduml
🛠 To render this:
- Use a PlantUML editor (e.g., PlantUML Live or PlantText).
- Paste the code in and click "Refresh" or "Render" to see the flowchart.
[1]Decision: Control flow construct in which a task is performed conditionally. Also referred to as selection.